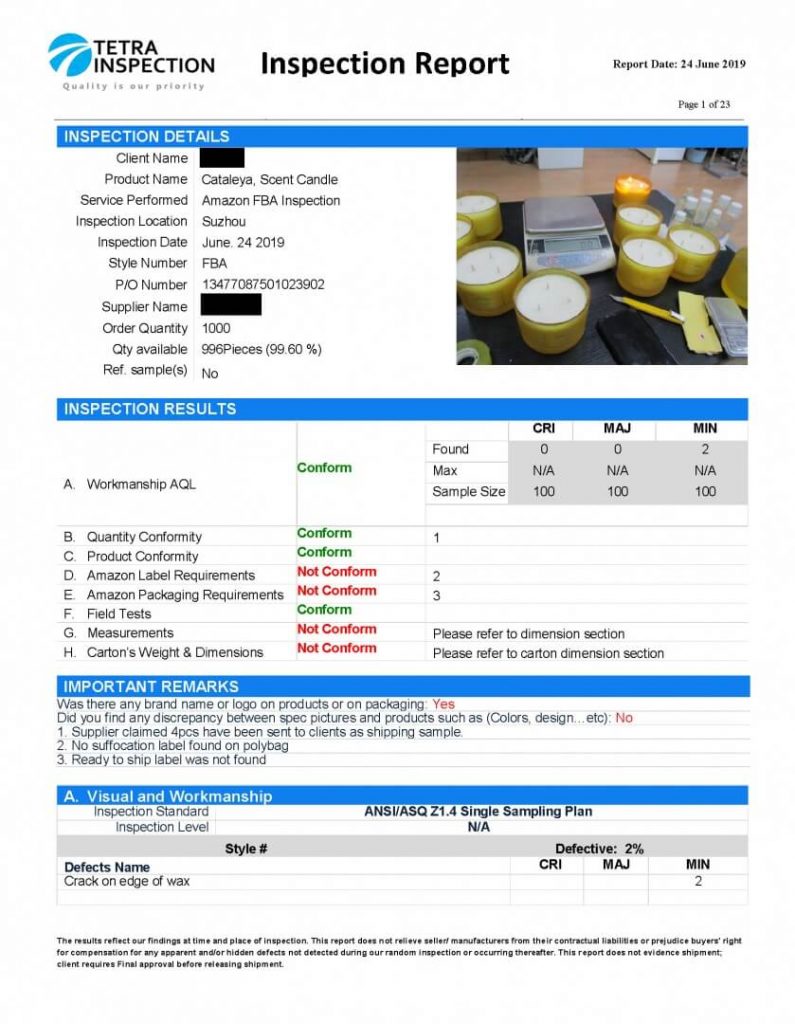
AQL Calculator Acceptable Quality Limit
Widely adopted international standard ISO2859-1
Even though the AQL chart and AQL table can help you breakdown the numbers, you will need an AQL calculator to get the numbers quickly and enhance accuracy. The AQL calculator is a simple and highly convenient tool to calculate the required sample size quickly. You only need to input your lot size, inspection level, inspection type, and limits. The calculator will provide you with an accurate sample size according to the AQL standard. Using the AQL calculator is an effective way to streamline your AQL sampling process.
At Tetra Inspection, we are dedicated to helping importers, suppliers, and manufacturers to access the insight, services, and tools they need to streamline AQL sampling and inspection. You can rely on our AQL calculator to determine your AQL sample size for inspection. Tetra AQL calculator is robust, accurate, and also allows you to determine the number of tolerated defects by selecting the appropriate AQL Level. It is easy, simple, and accurate.
How is AQL applied in practice?
Once an AQL standard is agreed on, it will be used as a reference during pre-shipment inspections. To determine the acceptable percentage for each type of defect in shipment.
Critical defects
Major defects
Minor defects

Critical Defects
The criteria for defining a critical defect are:
- Pose a safety hazard to the expected user
- Cause product recalls
- Brand damaging defects
Example of critical defects:
- Mold
- Broken needle in a garment
- Rusty items
- Exposed nails or sharp edges

Major Defects
Less serious than critical defects, major defects are usually accepted in limited quantities. Typically, importers will assign the AQL standard limit.
The criteria for defining a Major defect are:
- Affects the performance or function of a product
- Affects product specifications
- Causes the end customer to not buy or return the product
Example of major defects:
- Holes or tears on a fabric
- Out of tolerance dimensions for industrial components
- Uneven legs in an item of furniture
- Excess glue on a footwear item

Minor Defects
Most importers use AQL standard of 4.0 for minor defects, this is the least serious defect category, however, it can still cause the rejection of your order if found in large quantity.
The criteria for defining a minor defect are:
- It doesn't affect the function or use of the product
- Barely noticeable at arm distance
- Would be unlikely to cause a return or make the product unsellable
Example of minor defects:
- Untrimmed threads on a garment or plush toy
- Minor color shading
- Removable small dust
- Hidden dent mark
What's an AQL Table?
Acceptable Quality Limit table refers to the ANSI ASQ Z1.4 table used by QC inspections professionals for AQL sampling during the inspection. This AQL sampling plan is designed to help in determining the right sample size for inspection and the acceptable number of defects. Insight into the dynamics of the AQL table can also enhance your understanding and the interpretation of inspection results. It is vital for data-driven decision-making.
How to use AQL sampling plan table
While the AQL sampling plan table might seem intimidating, it is easy to use. It is divided into three columns for lot or batch size, sample size code letter, and sample size level I, with one larger section on the right for AQL. The AQL section consists of three sub-sections for AQL 2.5, AQL 4.0, and AQL 6.5, with Acceptable (Ac) and Rejectable (Re) column each.
AQL stands for “Acceptance Quality Limit” and indicates the percentage of defective units compared to the total units in a batch, order, or shipment. In ISO 2859-1, AQL is defined as the “quality level that is the worst tolerable.” It is an important statistical tool for quality control that leverages the capabilities of the Six Sigma methodology developed by Motorola. Quality control professionals can help importers doing business with manufactures and suppliers overseas to conduct pre-shipment inspections. The inspector checks for quality issues related to performance, usability, functionality, and aesthetics by inspecting a sample of the entire shipment. An inspection certificate is issued to certify that products meet the quality levels.
Importers and suppliers operating in the global marketplace have to adopt strict inspection in quality control measures to avoid issues down the line. While tapping overseas production is vital for success in the globalized market of the 21st century, it comes with numerous pitfalls. Determining the quality of the products before shipping is the biggest challenge facing importers and suppliers. To ensure each shipment meets quality level, importers, suppliers, manufacturers, and shipment inspection companies can use AQL.
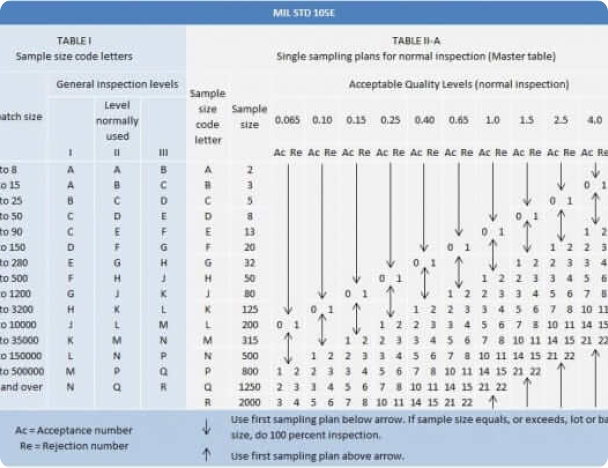
AQL sampling plan table
You only need the number of units in your order or shipment and countercheck with the parameters on the lot or batch size column. Find the accurate range where the units in your shipment or order fall. If your order has 2000 units, it will fall on 1,201-3,200 range in the lot or batch size column. This lines up with the letter “K” on the sample size code letter column and 125 units on the sample size level I. For your order of 2000 units, you will need to sample 125 units and determine whether it is acceptable or rejectable based on the corresponding numbers on the AQL section:
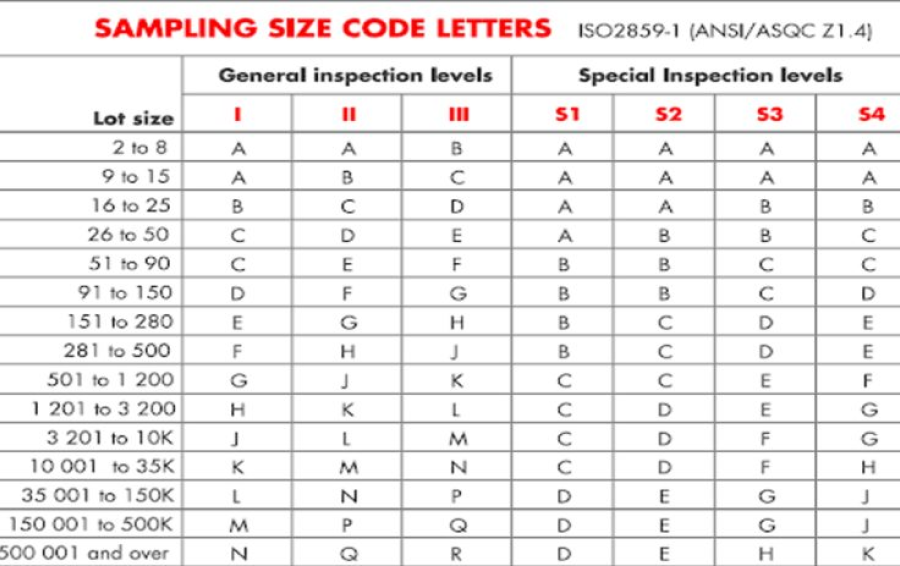
What is the AQL chart, and how does it work?
Table 1 on the AQL chart is Sample Size Code Letters, which is divided into three columns for lot or batch size, special inspection levels, and general inspection level. The special inspection levels column is reserved for particular types of product testing. The lot or batch size column represents the number of units in your order. If your order is 2000 units, it will fall between 1,201 and 3,200 in the lot or batch size column.
AQL Sampling table in AQL chart
Even though the general inspection levels consists of level I, II, and III, the best practice is to use level II (GII). Your selection for 2000 units from the lot or batch size column will correspond with K in the GII. Once you attain “K” as your sample size code letter, you can proceed to Table 2 on the AQL chart.
Table 2 on the AQL chart has three columns for sample size code letter, sample size, and acceptable quantity levels. The letter ‘K’ from Table 1 goes on the sample size code letter column of Table 2. It lines up with 125 units as the AQL sample size for the inspection.
AQL for normal inspection table
AQL 4.0 in normal inspection table Any critical defects are rejection table.
Once you’ve acquired the accurate AQL sample size and the AQL limits for your order, you can use this normal inspection table to conduct AQL inspections.
What is AQL inspection?
The quality limits and AQL sample size will guide your AQL inspection and help the inspector to decide whether to pass or fail the shipment.
After completing the AQL inspection, the inspection agency will issue a shipment inspection certificate. It certifies that the products pass the quality level and accompanies the shipment until it is delivered to you.